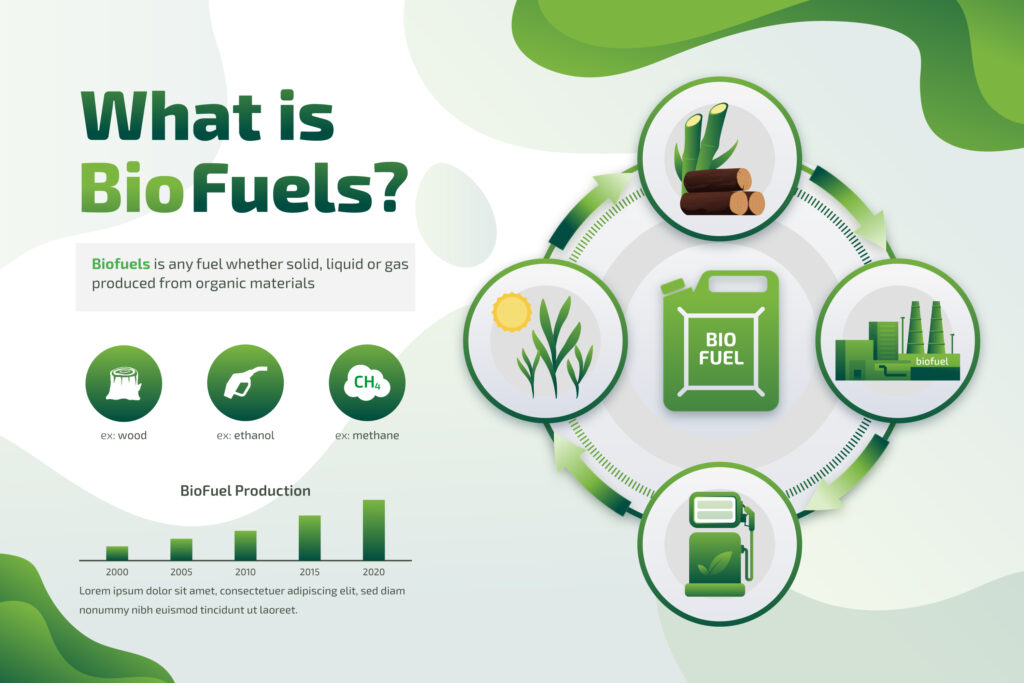
In a significant push toward clean energy and environmental sustainability, the Government of Madhya Pradesh has officially launched an ambitious Biofuel Promotion Scheme aimed at encouraging the production and use of biofuels across the state. This initiative is not only designed to reduce dependence on fossil fuels but also to generate employment and enhance the income of farmers by turning agricultural waste into valuable energy resources.
The scheme was unveiled by Chief Minister Shivraj Singh Chouhan at a state-level renewable energy conclave in Bhopal. The event, attended by farmers, energy entrepreneurs, scientists, and environmental activists, showcased the state’s roadmap toward a green energy future.
A Green Leap Toward Self-Reliance
Speaking at the launch, CM Chouhan said, “This is not just a fuel program; it’s a mission to empower our farmers, clean our environment, and create new avenues of employment. With this initiative, we aim to transform agricultural by-products and waste into a resource that fuels the future.”
Under the scheme, the state government will facilitate the setup of biofuel plants — including biodiesel, bioethanol, and biogas units — in both rural and semi-urban areas. The emphasis will be on using non-edible oil seeds, agricultural residue (such as sugarcane bagasse, rice straw, wheat husk), and organic waste as raw materials for biofuel production.
Key Objectives of the Biofuel Scheme
- Promote Sustainable Fuel Sources
The scheme aims to reduce the state’s reliance on imported fossil fuels by promoting locally produced biofuels. This aligns with India’s broader national objective of blending 20% ethanol with petrol by 2025. - Empower Farmers and Rural Communities
Farmers will be incentivized to supply biomass and crop residues to biofuel units. This ensures they receive value for agricultural by-products that would otherwise go to waste or be burned — a major contributor to air pollution. - Reduce Environmental Pollution
By encouraging the utilization of crop waste, the scheme targets the long-standing issue of stubble burning, especially in northern India, which causes severe seasonal air pollution. - Foster Rural Entrepreneurship
Financial and technical support will be provided to entrepreneurs and cooperatives for setting up decentralized biofuel production units in rural areas.
Financial Support and Incentives
The scheme includes capital subsidies, low-interest loans, and tax exemptions for eligible biofuel projects. The state government has allocated an initial budget of ₹250 crore for the fiscal year 2025–26 to kickstart the initiative.
Key highlights include:
- Up to 50% capital subsidy for small-scale biofuel plants.
- Priority land allotment and single-window clearance for new projects.
- Training and capacity-building workshops for farmers and local entrepreneurs.
In addition, the Madhya Pradesh Bio-Energy Development Board (MPBEDB) will serve as the nodal agency for overseeing implementation, monitoring progress, and coordinating between different departments and stakeholders.
Encouraging Private Sector Participation
Recognizing the role of private innovation and investment, the state government is also inviting public-private partnerships (PPP) and collaboration with startups and clean tech companies.
“We welcome investors and companies that can bring in technology and efficiency. This is an open platform for green growth,” said Pradyumna Singh Tomar, Minister of Energy and Renewable Resources.
Pilot Projects and Impact on Ground
Pilot projects have already been initiated in districts like Indore, Jabalpur, and Sehore, where small-scale biogas units and biodiesel production plants are operating with support from local farmer cooperatives. Initial reports show a 15–20% increase in farmer income in these areas due to waste-to-energy conversion.
In Indore, a successful collaboration between the municipal corporation and a private firm has resulted in a bio-CNG plant that processes over 400 tons of organic waste daily, generating enough clean energy to power city buses.
The success of these pilots is being used as a model to scale the initiative across the state.
Challenges and the Road Ahead
Despite the optimistic start, the scheme is not without challenges. Experts point to issues like:
- Lack of awareness among rural communities.
- The need for a robust supply chain for biomass collection.
- Infrastructure gaps in remote areas.
- Need for consistent government support and market access for biofuel products.
However, the government has assured continuous stakeholder engagement and policy flexibility to address these concerns.
Environmentalists have lauded the scheme as a step in the right direction. “Biofuels offer a way to decarbonize sectors like transportation and agriculture. It’s heartening to see a state government take a proactive approach,” said Dr. Anjali Menon, an environmental policy expert.
A Step Toward India’s Climate Commitments
Madhya Pradesh’s biofuel initiative comes at a time when India is striving to meet its Net Zero Emissions target by 2070 and fulfill commitments made under the Paris Agreement. The central government has been actively pushing for biofuel blending programs, and state-level initiatives like this one are crucial to reaching those national goals.
Conclusion
With its Biofuel Promotion Scheme, Madhya Pradesh has positioned itself as a leader in India’s green energy transformation. The initiative not only promises economic gains and environmental benefits but also sets a powerful example of how local solutions can contribute to global climate action.
As the state gears up to implement the program across more districts, all eyes will be on how effectively it can bridge the gap between policy and practice — and how many lives it can positively transform along the way.